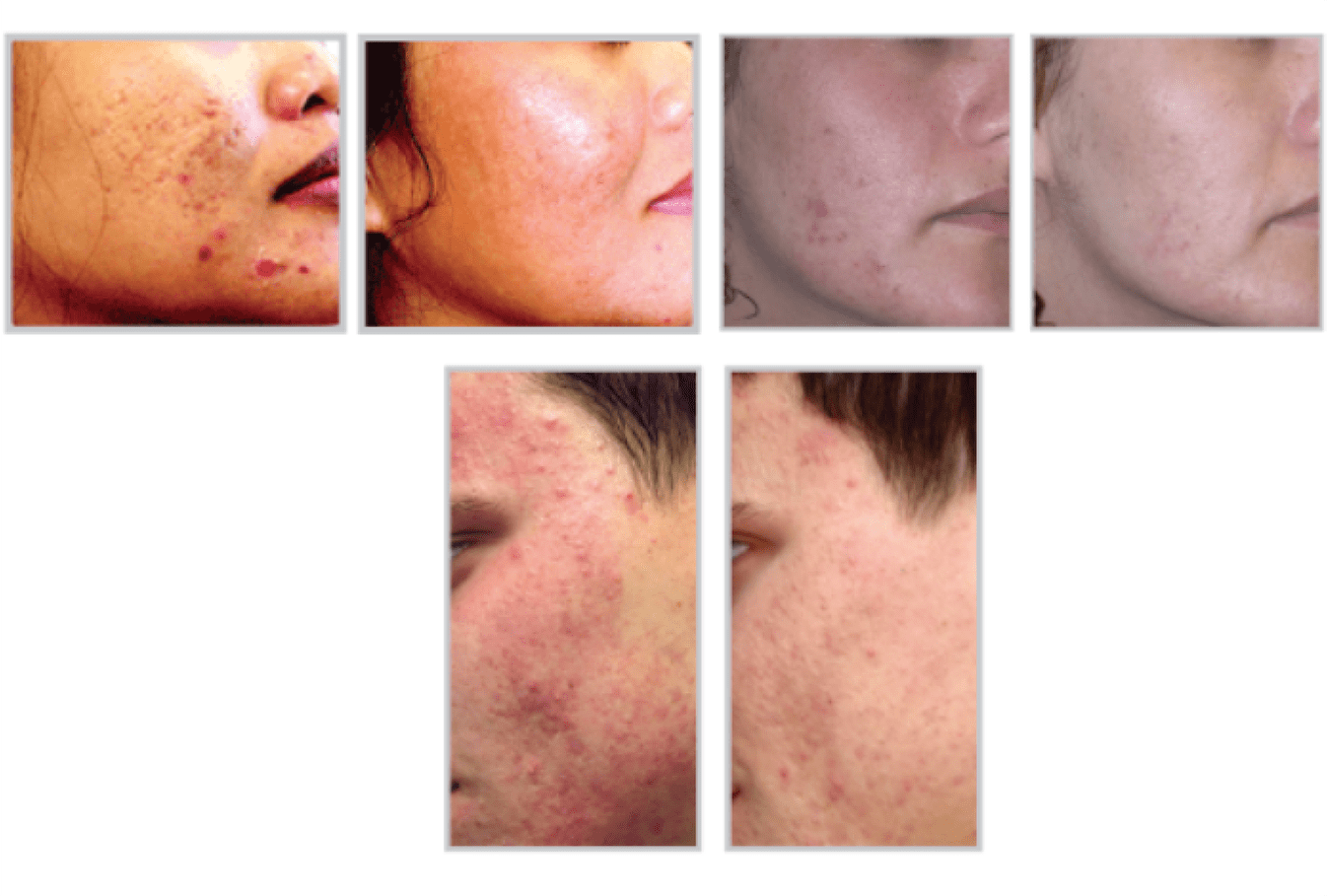
Acne is a disorder resulting from the action of hormones and other substances on the skin’s oil glands, sebaceous glands and hair follicles.
Acne is a disorder resulting from the action of hormones and other substances on the skin’s oil glands, sebaceous glands and hair follicles. Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) are the anaerobic bacterium that causes acne. Severe acne can lead to permanent scarring and emotional distress. Fortunately, several acne therapy options are available.
Chemical peels as well as Microdermabrasion, combined with blue light therapy, may provide significant benefits. Infrared energy and Photofacials can be combined to allow controlled heating of sub-epidermal layers of the skin. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is another area that holds promise. It involves administering a topical photosensitizing agent and then subjecting the area to a blue light. Doing so causes the release of free oxygen radicals, which can destroy the organism Propionibacterium acnes. Some acne therapy methods involve high intensity blue light without the photosensitizing agent. With proper treatment, the procedure will lead to collagen remodeling, proliferation of active fibroblasts and treating over-acting sebaceous glands that result inthe reduction of acne and the improvement in acne scarring.
For a more dramatic improvement, laser skin resurfacing may be recommended. Lasers are the newest and best methods proven effective nowadays for the treatment of acne and acne scarring. The wound-healing process produces fibroblasts that generate new collagen, plumping the skin and correcting skin imperfections.
Patient response can vary after a BBL Acne treatment. Erythema (redness) is usually noted within a few minutes after the completion of the procedure. A slight sunburn sensation in and around the area treated is also normal and expected. These reactions tend to subside within 1-4 hours after the treatment. Topical anesthesia is usually not required.
Contraindications:
- Patients with an abnormal response to sunlight.
- Patients using photo-sensitizing medications or drugs.
- Patients who have used Accutane within the last 6 months.
- Patients who are pregnant.
- Patients with tanned skin.
- Patients who have active infections or a history of skin cancer.
- Patients with a history of abnormal wound healing.
- Patients with pacemakers or implantable metallic devices.
Until sensitivity has completely subsided, avoid all of the following:
- Use of scented lotions or soaps, exfoliant creams (Retin-A, glycolic/salicylic and alpha- hydroxy acids), acne creams or gels, Loofa sponges and aggressive scrubbing.
- Hot or cold water – wash with tepid water.
- Shaving.
- Swimming pools and spas with chemicals/chlorine and/or severe temperature changes.
- Activities that cause excessive perspiration.